Penyedia perkhidmatan Internet (ISP)
-merupakan sebuah organisasi yang menyediakan akses kepada Internet.
-Pembekal perkhidmatan internet boleh menjadi sama ada milik masyarakat dan bukan mencari keuntungan, atau milik persendirian dan untuk keuntungan.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- adalah protokol permohonan untuk diedarkan, sistem, kerjasama maklumat hipermedia. [1] HTTP adalah asas komunikasi data untuk World Wide Web.
-mentakrifkan bagaimana mesej diformat dan dihantar, dan apakah tindakan pelayan Web dan pelayar harus mengambil sebagai tindak balas kepada arahan pelbagai.
Telecommunication And Networking..
Tuesday, 29 May 2012
Thursday, 26 April 2012
What is Network Cabling?
Cable is the medium through which information usually moves from one network device to another. There are several types of cable which are commonly used with LANs. In some cases, a network will utilize only one type of cable, other networks will use a variety of cable types. The type of cable chosen for a network is related to the network's topology, protocol, and size. Understanding the characteristics of different types of cable and how they relate to other aspects of a network is necessary for the development of a successful network.The following sections discuss the types of cables used in networks and other related topics.
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Cable Installation Guides
- Wireless LANs
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
Unshielded twisted pair
| Category | Speed | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 Mbps | Voice Only (Telephone Wire) |
| 2 | 4 Mbps | LocalTalk & Telephone (Rarely used) |
| 3 | 16 Mbps | 10BaseT Ethernet |
| 4 | 20 Mbps | Token Ring (Rarely used) |
| 5 | 100 Mbps (2 pair) | 100BaseT Ethernet |
| 1000 Mbps (4 pair) | Gigabit Ethernet | |
| 5e | 1,000 Mbps | Gigabit Ethernet |
| 6 | 10,000 Mbps | Gigabit Ethernet |
1.Unshielded Twisted Pair Connector
The standard connector for unshielded twisted pair cabling is an RJ-45 connector. This is a plastic connector that looks like a large telephone-style connector (See fig. 2). A slot allows the RJ-45 to be inserted only one way. RJ stands for Registered Jack, implying that the connector follows a standard borrowed from the telephone industry. This standard designates which wire goes with each pin inside the connector.2.Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
Although UTP cable is the least expensive cable, it may be susceptible to radio and electrical frequency interference (it should not be too close to electric motors, fluorescent lights, etc.). If you must place cable in environments with lots of potential interference, or if you must place cable in extremely sensitive environments that may be susceptible to the electrical current in the UTP, shielded twisted pair may be the solution. Shielded cables can also help to extend the maximum distance of the cables.
Shielded twisted pair cable is available in three different configurations:
- Each pair of wires is individually shielded with foil.
- There is a foil or braid shield inside the jacket covering all wires (as a group).
- There is a shield around each individual pair, as well as around the entire group of wires (referred to as double shield twisted pair).
3.Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cabling has a single copper conductor at its center. A plastic layer provides insulation between the center conductor and a braided metal shield (See fig. 3). The metal shield helps to block any outside interference from fluorescent lights, motors, and other computers.
4.Coaxial Cable Connectors
The most common type of connector used with coaxial cables is the Bayone-Neill-Concelman (BNC) connector (See fig. 4). Different types of adapters are available for BNC connectors, including a T-connector, barrel connector, and terminator. Connectors on the cable are the weakest points in any network. To help avoid problems with your network, always use the BNC connectors that crimp, rather screw, onto the cable.
5.Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cabling consists of a center glass core surrounded by several layers of protective materials. It transmits light rather than electronic signals eliminating the problem of electrical interference. This makes it ideal for certain environments that contain a large amount of electrical interference. It has also made it the standard for connecting networks between buildings, due to its immunity to the effects of moisture and lighting.
Fiber optic cable
| Specification | Cable Type |
|---|---|
| 10BaseT | Unshielded Twisted Pair |
| 10Base2 | Thin Coaxial |
| 10Base5 | Thick Coaxial |
| 100BaseT | Unshielded Twisted Pair |
| 100BaseFX | Fiber Optic |
| 100BaseBX | Single mode Fiber |
| 100BaseSX | Multimode Fiber |
| 1000BaseT | Unshielded Twisted Pair |
| 1000BaseFX | Fiber Optic |
| 1000BaseBX | Single mode Fiber |
| 1000BaseSX | Multimode Fiber |
6.Wireless standards and speeds
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a global, non-profit organization that helps to ensure standards and interoperability for wireless networks, and wireless networks are often referred to as WiFi (Wireless Fidelity). The original Wi-Fi standard (IEEE 802.11) was adopted in 1997. Since then many variations have emerged (and will continue to emerge). Wi-Fi networks use the Ethernet protocol.| Standard | Max Speed | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| 802.11a | 54 Mbps | 150 feet |
| 802.11b | 11 Mbps | 300 feet |
| 802.11g | 54 Mbps | 300 feet |
| 802.11n | 100 Mbps | 300+ feet |
Tuesday, 3 April 2012
Network topology
-Is the study of the arrangement or mapping of the element link,nodes etc.
Physical topology
Any given node in the LAN will have one or more links to one or more other nodes in the network and the mapping of these link and nodes onto a graph result in a geometrical shape that determines the physical topology of the network.
Logical topology
The mapping of the flow of data
1. Linear bus
2. Star
3. Star-wired ring
4. Tree
1.Linear bus
-continuos length of cable that connects TWO or MORE device together
BUS = backbone network
-only ONE computer can transfer info at a time
-The info moves through the entire length of a cable
each END of the cable must have a
TERMINATOR.
-device that absorbs the signals transmitted on a network cable
prevents signals from being bounced back along the cable and causing interference...
advantages
~ simple
~each computer is connected to a single length of cable
~often connected to a small area (office)
disadvantages
~expansion is exisiting can be difficult ! > cable must be broken to extend the cable and attach to the additional computer
~thus, other computer cannot exchange info
~if the computer is MALFUNCTIONING and causing problem on the cable > entire network will be infected !
~expensive ! most use a single piece of copper cable to connect its computers together
2.star
-central point on the network = HUB
-currently connectd to 4, 8 or 16 computers
-length between computers cable and hub must be LESS than 100m
advantages
~easy as long as there is a FREE port on the HUB
~no need to shut down when adding another computers
~when error occured, other computers not affected !
disadvantage
~hub fails = information can no longer transfer from one computer to another
~the COST is more implement than other types of network
~LARGE amount of cable is used because computer on the network must be independently connected to the hub
3.RING
-travels in ONE direction only
-information in transfer located next to it
-if it is not adress to the computer.then info will send to the next computer and so on
there is no beginning and end
Advantages
~ This type of network topology is very organized. Each node gets to send the data when it receives an empty token. This helps to reduces chances of collision. Also in ring topology all the traffic flows in only one direction at very high speed.
~ Even when the load on the network increases, its performance is better than that of Bus topology.
~ There is no need for network server to control the connectivity between workstations.
~ Additional components do not affect the performance of network.
~ Each computer has equal access to resources.
Disadvantages
~ Each packet of data must pass through all the computers between source and destination. This makes it slower than Star topology.
~ If one workstation or port goes down, the entire network gets affected.
~ Network is highly dependent on the wire which connects different components.
~ MAU’s and network cards are expensive as compared to Ethernet cards and hubs.
4.TREE
-Same with star and linear bus
-One type of star topology
-Also have terminator
-Hybrid(combine of 2 topology)
Advantage
Point to point for individual segments
Disadvantages
More difficult to configure and wire
Backbone line break,the intire segment goes down
Wednesday, 28 March 2012
What is Computer Networking?
•is connecting a computer with other computers or other devices to enable them to communicate with each other
Computer Networking
•LAN
Local Area Network
•MAN
Metropolitan Area Network
•WAN
Wide Area Network
Networking components can be categorise into
•Terminals, Workstations, Computers, and other devices (end nodes)
•Transmission Media ( for transmitting data and control signals)
•Network electronics ( intermediate devices for routing data from source to destination)
•Software to control data transmission
•Network Architecture Standards (Standards to enable devices made by different companies to work/communicate with each other.
TRANSMISSON MEDIA
•The physical media used to transmit data in a networked environment.
•To Transmit signal / electrical pulse through a medium.
•2 types : bounded/guided or unbounded/unguided
Bounded Media
1.Twisted pair wire
-type of wiring in which two conductors (forward and return circuit conductors a) twisted together for the purpose of canceling the electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources
2.Co-axial cable
3.Fiber optic cables
Unbounded Media (air or a vacuum)
1.AM and FM radio
-FM stands for "frequency modulation
-AM stands for "amplitude modulation," so it is not difficult to understand that our differences are based on radio caragelombang modulate, or volatility.
2.TV broadcasting
3.Satellite communication
4.Microwave radio
5.Infrared signals and bluetooth
-infrared is a communication system based on infrared light is used for short range communications applications line of sight or point-to-point, while
-Bluetooth is a low cost, low power, short-range radio technology was originally developed as a replacement cable to connect the various perantisepertitelefon mobile, headset, PDAs and laptops.
6.Bridge
-A network bridge connect multiple network segment.
7.Routers
-translates information from one network to another;it is similar to a superintelligent bridge.
8.Gateway
-A network node equipped for interfacing with another network that uses different protocol.
Monday, 12 March 2012
Data transmission is 6 type:
1. Analog vs digital
2 .Bandwidth
3. Serials Vs Parallel
4. Transmission timing
5. Transmission directions
6.Circuit switched, Packet‐Switched, and Broadcast
Connections
1.Analog
-Transmission uses signals that are exact replicas of a sound wave or image.
2.Digital
-Transmission the signals are converted into a binary code, which consists of two elements.
3.Bandwidth
-The amount of data that can be transmitted in a fixed amount of time.For digital devices, the bandwidth is usually measured in bits per second(bps), Megabits persecond (Mbps). Medium with higher bandwidth deliver data
faster.
4.serial and parallel
•Serial
data sent one bit at a time,one after another a long a single path
• Parallel
data is sent at least one byte at a time, each bit in the byte taking separate path
5.Transmission Timing
a)Synchronous transmission
Data organised into blocks or groups and transferred at regular specified interval
b)Asynchronous transmission
the process where transmitted data is encoded with start and stop bits, specifying the beginning and end of each character.Data sent without being synchronised
c)Isochronous transmission
data is sent at the same time as other related data to support certain types of real time applications e.g streaming voice, video and music.
data transmission mode
1. Analog vs digital
2 .Bandwidth
3. Serials Vs Parallel
4. Transmission timing
5. Transmission directions
6.Circuit switched, Packet‐Switched, and Broadcast
Connections
1.Analog
-Transmission uses signals that are exact replicas of a sound wave or image.
2.Digital
-Transmission the signals are converted into a binary code, which consists of two elements.
example of analogue and digital system:
3.Bandwidth
-The amount of data that can be transmitted in a fixed amount of time.For digital devices, the bandwidth is usually measured in bits per second(bps), Megabits persecond (Mbps). Medium with higher bandwidth deliver data
faster.
4.serial and parallel
•Serial
data sent one bit at a time,one after another a long a single path
• Parallel
data is sent at least one byte at a time, each bit in the byte taking separate path
5.Transmission Timing
a)Synchronous transmission
Data organised into blocks or groups and transferred at regular specified interval
b)Asynchronous transmission
the process where transmitted data is encoded with start and stop bits, specifying the beginning and end of each character.Data sent without being synchronised
c)Isochronous transmission
data is sent at the same time as other related data to support certain types of real time applications e.g streaming voice, video and music.
Sunday, 11 March 2012
WEEK 2
WEB BROWSER.
BOOKMARK (WORLD WIDE WEB)?




WEB BROWSER.
-is a software application that enables a user to display and interact with text, images, and other information typically located on a web page at a website on the World Wide Web or a local area network.
Examples of web browser::
- Mozilla Firefox,
- Apple Safari
- Netscape
- Opera
- Microsoft Internet Explorer and so on..
META-SEARCH ENGINE ?
-A metasearch engine is a search tool that sends user requests to several other search engines and/or databases and aggregates the results into a single list or displays them according to their source.
-Metasearch engines operate on the premise that the Web is too large for any one search engine to index it all and that more comprehensive search results can be obtained by combining the results from several search engines.
-This also may save the user from having to use multiple search engines separately.BOOKMARK (WORLD WIDE WEB)?
-In the context of the World Wide Web, a bookmark is a locally stored Uniform Resource Identifier (URI).
-All modern web browsers include bookmark features.
-Bookmarks are called favorites or Internet shortcuts in Internet Explorer.
-Bookmarks are normally accessed through a menu in the user's web browser, and folders are commonly used for organization.
-In addition to bookmarking methods within most browsers, many external applications offer bookmark management.
-All modern web browsers include bookmark features.
-Bookmarks are called favorites or Internet shortcuts in Internet Explorer.
-Bookmarks are normally accessed through a menu in the user's web browser, and folders are commonly used for organization.
-In addition to bookmarking methods within most browsers, many external applications offer bookmark management.
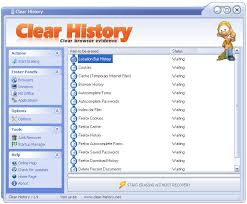
CLEAR HISTORY ??
-Clear History is free and powerfull windows desktop application to clean search history from your computer. It is full featured program that greatly surpasses most commercial programs out there.
WHAT IS CLEAR CACHE(VIDEO)?
-Cache files are nothing but regular files from web pages you visited, pictures, videos etc. Those files are used by browser instead of downloading again so your pages load faster.
-But, cache files are an evidence of where you have been and what you were doing on internet. So if you don't want your internet habits to be discovered you should clear cache on regular basis.
-To clear cache in your web browser is very straightforward - follow the instructions bellow.
-But, cache files are an evidence of where you have been and what you were doing on internet. So if you don't want your internet habits to be discovered you should clear cache on regular basis.
-To clear cache in your web browser is very straightforward - follow the instructions bellow.
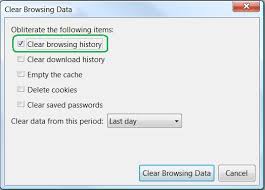
- Go to the Tools menu
- Select Clear Private Data
- Make sure Cache is checked. Uncheck others as you wish.
- Click on Clear Private Data Now and your cache is cleared.
CLEAR URL HISTORY ???
-If you don't clear URL history files, your web browser automatically keeps a detailed record of all web sites you've visited usually for more than forty days.
-The history feature enables you to have a more exact internet surfing experience. However if you want to eliminate only specific private searches from your URL history because there are other users of your PC who would like their URLs logged, you can selectively clear URL history files.If you don't clear URL history files, your web browser automatically keeps a detailed record of all web sites you've visited usually for more than forty days.
-The history feature enables you to have a more exact internet surfing experience. However if you want to eliminate only specific private searches from your URL history because there are other users of your PC who would like their URLs logged, you can selectively clear URL history files.
-The history feature enables you to have a more exact internet surfing experience. However if you want to eliminate only specific private searches from your URL history because there are other users of your PC who would like their URLs logged, you can selectively clear URL history files.If you don't clear URL history files, your web browser automatically keeps a detailed record of all web sites you've visited usually for more than forty days.
-The history feature enables you to have a more exact internet surfing experience. However if you want to eliminate only specific private searches from your URL history because there are other users of your PC who would like their URLs logged, you can selectively clear URL history files.
MULTITASKING ??
-The ability to execute more than one task at the same time, a task being a program.
In multitasking, only one CPU is involved, but it switches from one program to another so quickly that it gives the appearance of executing all of the programs at the same time.
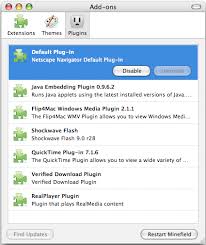
PLUG-IN ???
In computing, a plug-in (or plugin) is a set of software components that adds specific abilities to a larger software application.
-If supported, plug-ins enable customizing the functionality of an application.
-For example, plug-ins are commonly used in web browsers to play video, scan for viruses, and display new file types. Well-known plug-ins examples include Adobe Flash Player, QuickTime, and Microsoft Silverlight.
-If supported, plug-ins enable customizing the functionality of an application.
-For example, plug-ins are commonly used in web browsers to play video, scan for viruses, and display new file types. Well-known plug-ins examples include Adobe Flash Player, QuickTime, and Microsoft Silverlight.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)












